Did you know that Boswellia serrata or Shallaki is a decidous plant that is native to India which produces the fragrant resin commonly known as Indian olibanum, Indian frankincense?
Boswellia serrata or Shallaki with Latin name Olibanum Indicum is a tropical dry deciduous forest plant that is native to India, and its fragrant resin is commonly known as: Indian olibanum, Indian frankincense. Frankincense is also known as the Biblical incense, an extract from the resin of the tree Boswellia sacra, and is now produced also from B. frereana. The medicinal uses of the gum-resin extracts of Boswellia serrata have been traditionally used in herbal folk medicine for centuries to treat various chronic inflammatory diseases. The Indian version of this herbal medicine popularly cited as the indigenous herb, is 'Salai Guggal', the herbal Artiritic pain reliever, that is said to be, besides being natural and safer, also more effective.
Boswellia serrata is named for John Boswell, Scottish botanist of Edinburgh, England, with 'serrata' spelled "sair-AY-tuh or ser-RAT-uh' meaning "toothed like a saw". It is a deciduous medium sized tree, a genus of trees in the order Sapindales, known for their fragrant resin. It can grow to a height up to 18 m and up to 2.4 m in girth. Its leaves are alternate, exstipulate, imparipinnate, 20-45 cm in length and are like neem plant with the flowers which are bisexual bloom in white color. It bears fruits, drupe type, about 12 cm long with 3 seeds ovoid, trigonous; pyrenes. The gum derived from its bark and its flowers and seeds are together known as Indian Francineus. It is usually grown in red, lateritic to rocky soils of dry deciduous forests and on dry sand stone ridges. It grows well in dry, hot exposures of rocky hills, with 50-125 cm rainfall and is propogated through seeds. The resin present in the bark of Boswellia tree is Shellaki, which is its main medicinal product. However, its intense use has become a non-sustainable practice in recent years that has created a risk of being eradicated.
A single tree is reported to yield one to two kilograms of gum in a year. The gum is extracted by removing a small patch of bark. The resin is fragrant, transparent and golden yellow and on drying brownish yellow. Gum-resin contains 30-60% resin, 5-10% essential oils (soluble in the organic solvents) and the rest is made up of polysaccharides. Resin solidifies slowly with time to reddish brown, greenish yellow, or dull yellow to orange in color.
Research studies of Boswellia serrata indicate various derivatives as boswellic acid including β-boswellic acid, acetyl-β-boswellic acid, 11-keto-β-boswellic acid and acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid.
Apart from its English name of Boswellia serrata or Indian frankincense tree, Indian olibanum tree, the plant and its derived resin is known in Indian vernacualr langauges as : Shallaki (शल्लकी), Sallaki, Yakshadhupa, Salasiniryasam, Bhishan, and Bahusrava in Sanskrit and Hindi; Guggula mara ಗುಗ್ಗುಳ ಮರ Madi, Guggaladupa, Haalu maddi, chilakadupa, paramgi saambraani ಪರಮ್ಗಿ ಸಾಮ್ಬ್ರಾಣಿ in Kannada; Dhupamu, Guggilamu (గుగ్గిలము), Parangisambrani, Tellaguggilamu, Andugapisunu in Telugu; saaledi, સલાઈ ગૂગળ salaai gugul in Gujarathi; kungilyam കുങ്ങില്യം in Malayalam; loban ਲੋਬਾਣ in Punjabi; Kundurukkan, Kungiliyam குங்கிலியம், Kungli, Vellai kunkiliyam,vellai-k-kirai வெள்ளிக்கீரை in Tamil; and loban in Urdu.
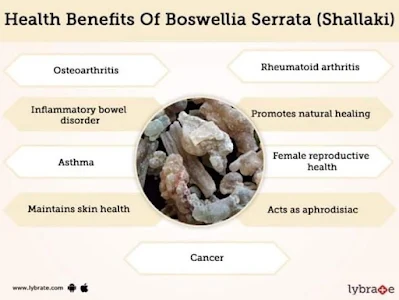
In Indain folk medicine, this herbal plant has known uses of its extracts (clinically studied) for diabetes, osteoarthritis and joint function. Its use as Salai guggal, or Boswellia serrata is reported to work amazingly to reduce inflammation and relieve pain. Its use in any form is recommended in small doses to avoid any adverse effects.
- Narasipur Char